-Dr. Rusnardi Rahamat Putra
Assistant Professor, Padang state University
Padang, Indonesia.
The Indonesian
archipelago is located at the boundary of three major tectonic plates, the Indo-Australian,
Pacific, and Eurasian plates, stretching from Sumatra in the west to Papua in
the east. Indonesia is at the collision point of these three crustal plates.
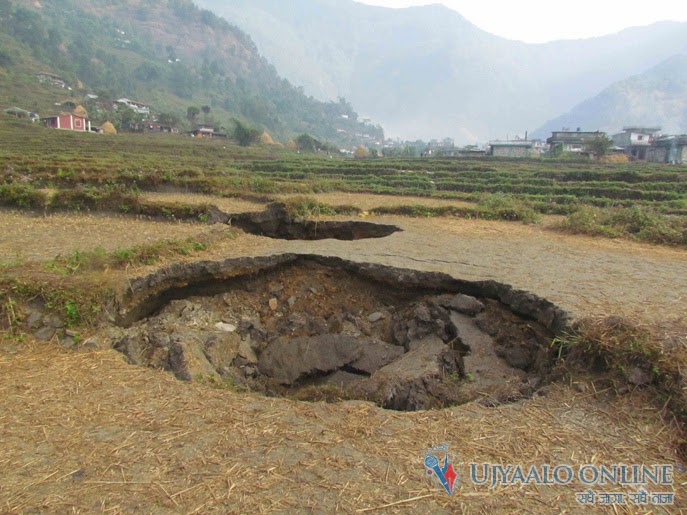
The high subduction-related seismicity in this region means that tsunami and
other earthquake hazards are also high. Indonesia has approximately 17,504
islands, with a total land area of 1.92×106
km2 and a sea area of 3.26×106 km2. It has experienced a large number of earthquakes in the past. According
to catalogued events, the number of earthquakes that have occurred in this region
exceeds 45,778 with a magnitude greater than 4.0 from AD 1779 to 2010.
Most of the
major historical earthquakes in Indonesia have caused significant damage to facilities
(e.g., Utsu et al., 1992; Fauzi et al., 1999; EERI, 2010). Many large
earthquakes have occurred in the shallow seas of the area that can produce massive
tsunami like the 2004 Banda Aceh event. This earthquake off the coast of
Sumatra resulted in hundreds of thousands of deaths and a million people
homeless (Ghobarah. A et al., 2006). Tectonic and plate boundaries, Large arrows indicate the direction of plate
motion.